Non Destructive Testing (NDT)

Authors: W.D. Dover, R. Collins, D. H. Michael
Ac-field measurement technique measures and interprets
field perturbations in a region containing a surface flaw.
ACPD, as it was originally called, has a long history of
malpractice but was so eminently suitable for laboratory
monitoring of fatigue cracks that it was reassessed for this
purpose. The technique consists of impressing an AC
current into the region containing the flaw and exploring
the surface—voltage distribution with a probe.


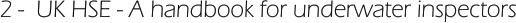
Initially edited in hard copy, this book was considered one
of the most relevant documents when published. Apart
from some new technologies that did not exist when it
was written, we can say that this document is still actual
and should be considered a reference.
Note that this is a big file, and downloading it takes time.



Authors: A.I.Bondarenko, E.O.Paton
Extended welded pipelines are characterized by the
presence of various discontinuities in them related to the
change of material density and/or cross-section of pipe
walls on their joint boundary and/or along the pipe
length. This paper deals with detecting these
discontinuities, with which low-frequency guided waves
of longitudinal and torsional modes interact during their
propagation in the form of a circular wave through the
pipe cross-section.



Author not indicated
Ultrasonic Testing (UT) uses high frequency sound energy
to conduct examinations and make measurements.
Ultrasonic inspection can be used for flaw
detection/evaluation, dimensional measurements, material
characterization, and more. To illustrate the general
inspection principle, a typical pulse/echo inspection
configuration as illustrated below will be used.

Author unknown
This presentation provides information on magnetic
particle inspection methods (MPI).
It can be used to teach divers on the purpose and
implementation of such procedures during mobilization
and maintenance. This document does not explain
underwater MPI.



Publisher: Mark Stephen Rogers
This presentation shows the applications, advantages and
disadvantages of various Non-Destructive Techniques
(NDT) used in multiple industries, particularly in the
offshore and petroleum industries.



This document can be classified under the “Technical
document - Vessels” rubric. Nevertheless, it provides
guidelines that can be used to organize inspections.



Author:
Reza K. Amineh, Maryam Ravan, Hesamedin Sadeghi, and
Rouzbeh Moini
In the alternative current field measurement (ACFM)
technique, the nonzero value of liftoff distance for the
magnetic sensor acts as a low-pass filter on surface crack
signals, causing errors in crack detection and sizing. The
authors present a blind deconvolution algorithm for Liftoff
evaluation and surface crack signal restoration.


Publisher: Siemens Rolling Stock Pvt. Ltd, Aurangabad
This presentation can be used to inform personnel on
ultrasonic testing



Publisher: International Atomic Energy Agency
Even though this document is not specifically designed for
diving activities, it provides essential information regarding
Eddy Current.



Publisher: Dzevad Hadzihafizovic
This handbook provides basic information about weld
conditions, gauges, symbols, and weld terms.




Authors:
Jasper A. Agbakwuru, Ove T. Gudmestad, John Groenli,
Helge Skjaveland
This paper demonstrates a technique for tracking and
identifying leaking points on pipelines installed in
unclear/muddy water conditions using optical cameras.
The method leads a remotely operated or hyperbaric
system to the leak in muddy water conditions for close
visual inspection and subsequent repair.




Authors:
Ken Woolley, Tim Woolley, and Bruce Banfield
Since the beginning, underwater MPI has been carried by
night due to the inks' characteristics. New inks are now
available, although they are for topside use and thus are
not necessarily applicable to underwater conditions.
Recent trials have been conducted to determine the
suitability of available inks to increase white light levels
underwater. This paper presents the work and discusses
the findings, which have application worldwide.



Publisher: Frontline
This document provides procedures for visual and optical
inspection according to “Frontline”, a company specialised
in non destructive techniques
(https://frontlinetesting.com/ )



Authors: Restu Putra & Ahmad Irsyad
This presentation is another document that can be used to
initiate personnel to Eddy Current inspection.




Author: Mark W Hounslow
Particulate matter derived from various fuel combustion
sources contains minor to trace amounts of Fe-oxides that
magnetic measurements can detect. These magnetic
particulates can be used as proxies for particulate pollution
since oxide contents are often more significant in
quantities and may have distinctive magnetic properties
compared to most types of natural dust.




Author:
Ali Khaloo , David Lattanzi, Adam Jachimowicz, and
Charles Devaney
This paper presents a case study where photogrammetry
was used to create comprehensive and high-resolution
3D point clouds of a dam and surrounding environment
at intervals. These models were then assessed for their
quality and ability to resolve defects that were artificially
applied to the structure between inspection intervals. The
results indicate that the integrated process can generate
models that accurately render various defect types with
sub-millimeter accuracy.




Authors: Restu Putra & Ahmad Irsyad
This presentation is another document that can be used
to initiate personnel to Eddy Current inspection.





Publisher: International Atomic Energy Agency
Even though this document is not specifically designed for
diving activities, it provides essential information regarding
the use of NDT .
The organization for which it has been designed is proof
of quality.




This is another document from the International Atomic
Energy Agency, not specifically designed for diving
activities, that provides essential information regarding the
use of NDT.






Tomography is an x-ray technique in which shadows of
superimposed structures are blurred out by a moving x-ray
tube. This method is used in radiology, archaeology,
biology, atmospheric science, geophysics, oceanography,
plasma physics, materials science, astrophysics, quantum
information, and other areas of science.
This document is provided by the International Atomic
Energy Agency.





Click on the
octopus to return to
the top of the page

Authors: Duje Medak, Luka Posilovic, Marko Subasic,
Marko Budimir, Sven Loncari
Most ultrasonic data collection has recently become
automated, but the analysis of this data is still done
manually. This makes it expensive, inconsistent, and prone
to errors. An automated system could make processes
much more efficient, but the current methods are not
effective. Deep learning could be a more effective
approach for analyzing this data, as it has been successful
in similar cases. Based on this, the authors utilized a deep
learning model called EfficientDet to automatically detect
defects in ultrasonic images.


Authors: Chao Chen, and Xingyuan Zhang
A support vector machine-based method is proposed to
solve the challenge of accurately quantifying surface
defect depth during laser ultrasonic inspection. A finite
element model for laser ultrasound inspection of
aluminum materials with surface defects was developed
using COMSOL software, based on the thermal-elastic
mechanism.


Authors: Xiaofei Li, Heming Sun, Taiyi Song, Tian Zhang,
Qinghang Meng
This study focuses on the detection and identification of
structural cracks in underwater bridge structures using
advanced image recognition networks. It compares
different networks and outlines the methodology,
including ablation experiments to evaluate the
performance and accuracy of various network
combinations in identifying underwater structural
damage.


Authors: Sheng Shen, Zheng Cao, & Changqin Lai
This document describes the development of a sonar
scanning scheme designed explicitly for inspecting
underwater high-rise pile cap foundations (HRPCFs). The
goal is to enhance the efficiency of bridge inspections and
extend the structural durability of these foundations. It
discusses the experimental determination of critical factors
affecting sonar measurement accuracy, the design of a
platform to hold and move the sonar device under strong
currents, and the strategy for optimal placement of
measurement points to avoid signal obstruction.


Authors: Zehao Wang, Defeng Zheng, Xingsen Guo,
Zhongde Gu, Yueqiang Shen, & Tingkai Nian
This study explains the impact of submarine landslides on
underwater structures, focusing on bucket foundations. It
introduces a fluid-structure coupling system using the
coupled Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH)-Finite
Element Method (FEM) to analyze the displacement
response of these foundations during landslide impacts.
The research aims to provide a new numerical simulation
approach and offers insights into underwater structures'
dynamic response and failure mechanisms under extreme
conditions.


Authors: Hao Wang, Kan Wang, Xiaolei Liu, Yang Liu,
Zhijia Qian, and Sheng Ding
This study explains the development and analysis of an
offshore floating photovoltaics (FPV)-based hydrogen
production system. It addresses the challenges, particularly
safety concerns, associated with hydrogen storage in such
systems. It involves creating a numerical 3D model to
investigate the characteristics of accidental damage and
hydrogen release under different offshore wind
conditions. It also explores the dynamic development of
hydrogen dispersion and evaluates the evolution of
thermal hazards and damage in the marine environment.



Publisher:
UK-HSE
This document is designed to guide plant engineers and
inspection personnel on methods for analyzing and
extrapolating inspections for large plant items, including
vessels, pipework, and pipelines, while considering the
statistical nature of corrosion. It aims to introduce methods
of statistical analysis of corrosion inspection data. Before
incorporating the methodology into standards, practical
experience in industrial applications is necessary to identify
the most relevant distributions and statistical techniques.




Publisher: UK HSEi
The document intends to inform the reader about the
importance of ultimate strength analysis in assessing the
robustness of offshore platforms and how this analysis can
be used to optimize inspection planning. It highlights the
role of EQE International, Inc. in conducting a study for
the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) to explore the
relationship between platform robustness and inspection
requirements.



This document describes the process and methodology of
the specific inspection project, Key Programme 3,
conducted by the HSE Offshore Division between 2004
and 2007. It explains how inspections were carried out,
the scoring system used (traffic lights), the roles of the
inspectors, and how the results were evaluated and
recorded, and provides an overview of the inspection
process, including the criteria for compliance and the
evaluation of safety-critical elements.



Author: Junfeng Fan, Yaming Ou, Xuan Li, Chao Zhou,
and Zengguang Hou
This document describes a new method for inspecting
underwater pipelines using underwater vehicles equipped
with structured light vision (SLV) technology. The text
outlines the limitations of current inspection methods and
introduces a proposed solution that involves a dual-line
laser SLV system. This system aims to improve precision,
resolution, and information capture for fine three-
dimensional reconstruction of underwater pipelines. The
text also highlights the integration of this technology with
the BlueROV underwater vehicle and presents
experimental results demonstrating the effectiveness of the
method.


Author: Hwei-Yang Tan
This study develops a new approach for analyzing
corrosion in the oil and gas industry, addressing limitations
in current industrial practices and standards by
incorporating statistical methods that account for various
risk factors and the stochastic nature of localized corrosion.
It improves the prediction of the remaining useful life of
components in oil and gas plants by utilizing advanced
statistical techniques and software.





Authors: Franka Nauer, and Peter Kampmann
This paper analyzes the current state and challenges of
autonomous underwater intervention technology,
particularly focusing on the use of intervention
Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) for inspection
and maintenance of underwater infrastructure. It identifies
key requirements and challenges in the development of
high-level autonomy for these vehicles, such as decision-
making, tool handling, and precise navigation, and further
research and development in this field.



It can also be downloaded through this link:
https://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/ukgwa/20230
103120103/https://www.hse.gov.uk/research/otipdf/oti8
8539.pdf
Authors: Dr. John M. Webster. Dr Thanga Thevar. Tim
Schmidt. Jackie Mew
Corrosion in aluminium aircraft structures is a growing
issue in the aging fleet, which may affect safety. Existing
methods for detecting hidden corrosion are often slow
and not very accurate. Techniques like Thermal Wave
Imaging show promise, but challenges remain. Reliable
detection methods are still being developed, with early
results from Remote Acoustic Impact Doppler (RAID)
technology being presented.


3 - A New Computational Imaging Method for the Remote
Detection and Quantification of Hidden Corrosion

Authors: R. Raisutis, E. Jasituniene, R. Sliteris, A.
Vladisauskas
Wind power is a clean and renewable energy source
that requires regular inspection of wind turbine
components. This study reviews techniques for
monitoring and non-destructive testing (NDT) of wind
turbine blades, including vibration analysis,
thermography, X-ray imaging, acoustic emission, and
ultrasound. The goal is to assess various NDT methods
suitable for the complex structures of blades and harsh
conditions.


13 - The review of non-destructive testing techniques suitable for
inspection of the wind turbine blades

Authors: Peter W. Tse and J.M. Chen
The steel wire ropes used in elevators can rust and crack
due to exposure to salty air. Poor maintenance often
leads to accidents from broken wires. Current inspections
rely on human visual checks, which miss faults, especially
under grease. This study proposes an ultrasonic guided
wave technique for better detection of wire faults. Results
show that this method can find broken wires effectively,
even on greasy ropes, but needs further refinement for
on-site testing. Future research should focus on
improving operational parameters and developing
practical sensors.

20 - Effective Guided Wave Technique for Performing Non-
destructive Inspection on Steel Wire Ropes that Hoist Elevators


Authors: Oleg Gaidai, Yu Cao, Yan Zhu, Fuxi Zhang, and
Hongchen Li
A new reliability method suitable for multi-dimensional
structural dynamics is introduced in this study, using the
Gaidai multivariate method on an offshore Jacket
platform in Bohai Bay. It estimates collapse risks under
environmental stress, addressing challenges of high
dimensionality and nonlinear correlations. This method is
essential for offshore engineers during design to assess
operational failure, damage, or hazards.


36 - Multivariate Risk Assessment for Offshore Jacket Platformsby
Gaidai Reliability Method.

Authors: Jingzhou Xin, Guangjiong Tao, Qizhi Tang, Fei
Zou, Chenglong Xiang
This study proposes a new damage identification method
using Swin Transformer and continuous wavelet
transform (CWT). It converts structural vibration data into
a time-frequency diagram to capture damage
characteristics. The Swin Transformer extracts damage
information from this diagram. The method's accuracy is
analyzed with various sample lengths and noise levels,
confirming its robustness. Laboratory tests show it
recognizes damage with 99. 6% accuracy for single
damage and 99. 0% for multiple damages.


37 - Structural damage identification method based on Swin
Transformer and continuous wavelet transform.


Authors: Andrei Nazarov, Tatiana Yurasova, and Andrey
Marshakov
This review examines how different aqueous electrolytes
impact hydrogen absorption and self-corrosion in
magnesium anodes. It discusses historical and recent
studies on mechanisms of self-corrosion and hydrogen
evolution under specific effects. The focus is on
magnesium hydride formation and oxidation during
active dissolution and how anodic dissolution occurs
through protective films in other conditions. It also looks
at factors influencing hydride formation and self-
corrosion.


39 - Hydrogen Absorption and Self-Corrosion of Mg Anode:
Influence of Aqueous Electrolyte Species


Authors: Yuheng Chen, Haicheng Zhang, Weisheng
Zou, Haihua Zhang, Bin Zhou, Daolin Xu
This study proposes a new ROV-based deep-sea mining
system to address slippage and sinking issues of
traditional vehicles. A learning-based control strategy is
introduced, utilizing a nonparametric learning method to
improve path-tracking performance.


40 - Dynamic modeling and learning based path tracking control
for ROV-based deep-sea mining vehicle.


Authors: Beate Oswald-Tranta
Inductive thermography is a strong inspection method for
finding defects in metals. The technique has improved
over decades from lab tests to industry use. This paper
reviews its theory and key technical aspects. While it can
find various defects, the focus is on detecting surface
cracks in metals, with examples of current industrial
applications.


41 - Inductive thermography – review of a non-destructive
inspection technique for surface crack detection


Authors: Mohammadebrahim Bajgholi, Gilles Rousseau,
Denis Thibault, Simon Francoeur.
This study evaluates advanced Non-Destructive Testing
(NDT) techniques for detecting flaws in welded repairs of
martensitic stainless steel plates, focusing on Francis
turbine runners. Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing (PAUT),
Total Focusing Method (TFM), and Eddy Current Array
(ECA) technologies were examined to assess repair
integrity and identify flaws such as lack of fusion (LOF).
The findings highlight the necessity of integrating
advanced NDT techniques to ensure the structural
integrity of critical components, particularly in high-stress
applications such as turbine runners.


43 - Advanced Non-Destructive Testing Techniques for Welded
Joint Repairs: A Case Study on Improving Inspection Reliability
and Structural Integrity Assessment


Authors: Luca Paterlini, Andrea Marinelli, Andrea Brenna
and Marco Ormellese
This document proposes a risk map to manage
phenomena linked to the fact that carbon steel structures
that transport hydrocarbons have systems to prevent
corrosion, including cathodic protection and insulating
coatings, and that electrical interference, both AC and DC,
can cause corrosion even with protection applied.


44 - Protection Criteria of Cathodically Protected Pipelines Under AC
Interference.




45 - Natural van der Waals canalization lens for non-destructive
nanoelectronic circuit imaging and inspection

Authors: Qingdong Ou, Shuwen Xue, Weiliang Ma,
Jiong Yang, Guangyuan Si , Lu Liu, Gang
Zhong, Jingying Liu, Zongyuan Xie, Ying Xiao,
Kourosh Kalantar-Zadeh, Xiang Qi, Peining Li,
Zhigao Dai, Huanyang Chen, Qiaoliang Bao
Optical inspection is important in semiconductor wafer
manufacturing for analyzing surfaces and defects.
Traditional methods struggle with resolution and
detecting buried structures. The authors suggest a new
approach using a van der Waals canalization lens from a-
MoO 3 crystals, achieving 15 nm resolution for both
surface and buried imaging. This method offers better
imaging without the issues faced by other lenses,
enabling high-resolution inspection of buried nanoscale
circuits, crucial for future semiconductor manufacturing.

Authors: Andrzej Katunin, Krzysztof Dragan, Marko
Nagode, Krzysztof Lis, Kamil Joszko, Adam
Cholewa, Jernej Klemenc, Simon Oman, Paweł
Zak, Piotr Synaszko
Hidden corrosion, if not found quickly, can greatly
impact the strength and safety of aircraft. Enhancing
non-destructive testing (NDT) methods is crucial for safe
aircraft operation. The D-Sight technique is commonly
used for detecting this corrosion, valued in the
aerospace industry for its fast and low-cost inspections.
One of the drawbacks


46 - Towards quantification of hidden corrosion using D-Sight non
destructive testing technique


Authors:
Emmanuella Onyinye Nwulu, Tari Yvonne Elete,
Friday Emmanuel Adikwu, and Fidelis Othuke Onyeke
The durability of coatings is crucial for protecting
infrastructure from damage. This study suggests a
framework using advanced non-destructive testing
(NDT) technologies for inspecting coating durability. It
incorporates methods like ultrasonic testing and data
analytics to find defects and predict lifespan. Case studies
show this approach improves decision-making and saves
costs. The framework promotes better inspection
practices across different sectors for enhanced
performance and sustainability.


42 - Advancing inspection techniques for coating durability: A
framework for integrating non-destructive testing technologies.












